73
TECH
tip
by BLUE SEA SYSTEMS
THE NUTS AND BOLTS OF ANY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM ARE
THE CONNECTORS WHICH KEEP THE CURRENT FLOWING.
Blue Sea Systems connectors reduce heat and improve efficiency
and reliability in a boat’s electrical system.
The features below make Blue Sea Systems connectors stand out
from the others:
Tin-plated copper buses
provide maximum conductivity and
corrosion resistance.
Insert-molded stainless steel studs
eliminate the need
for securing nuts and allow high torquing for excellent electrical
contact.
UL 94-V0 rated base materials
resist high heat.
Terminal Screws
incorporate stainless steel split ring lock
washers and captive star-type lock washers keep connections
tight in high vibration environments.
One-Piece Serrated Flange Nuts
ensure correct and
secure connections
Optional insulating covers
meet ABYC and USCG
insulation requirements.
C
O N N E C T O R S A N D
I
N S U L A T O R S
TECH
tip
by BLUE SEA SYSTEMS
How a BusBar Should be Rated
Until now, there was no consistent method of rating busbars
which made it difficult to determine the appropriate busbar for
the application. The American Boating and Yacht Council (ABYC) is
considering adding busbar ratings to the Electrical Section E11. Other
organizations, including the Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers (IEEE), currently offer guidance.
The IEEE states a busbar should be rated at the highest
amperage passing through any section of the busbar,
with a maximum of a 50° C rise in temperature from an
ambient temperature of 50° C.
Blue Sea Systems uses a more conservative threshold of a 40° C rise
in temperature since busbars are often located in hot engine rooms.
This rating method avoids excess terminal temperature at the wire
termination.
Factors Influencing BusBar Ampacity Ratings:
1) Material:
The rating of any busbar is based on both the cross
section of the bus and the material used. Blue Sea Systems
uses Tin-Plated Copper C11000 which has more than
3.5 times the electrical conductivity as brass, used by
some manufacturers.
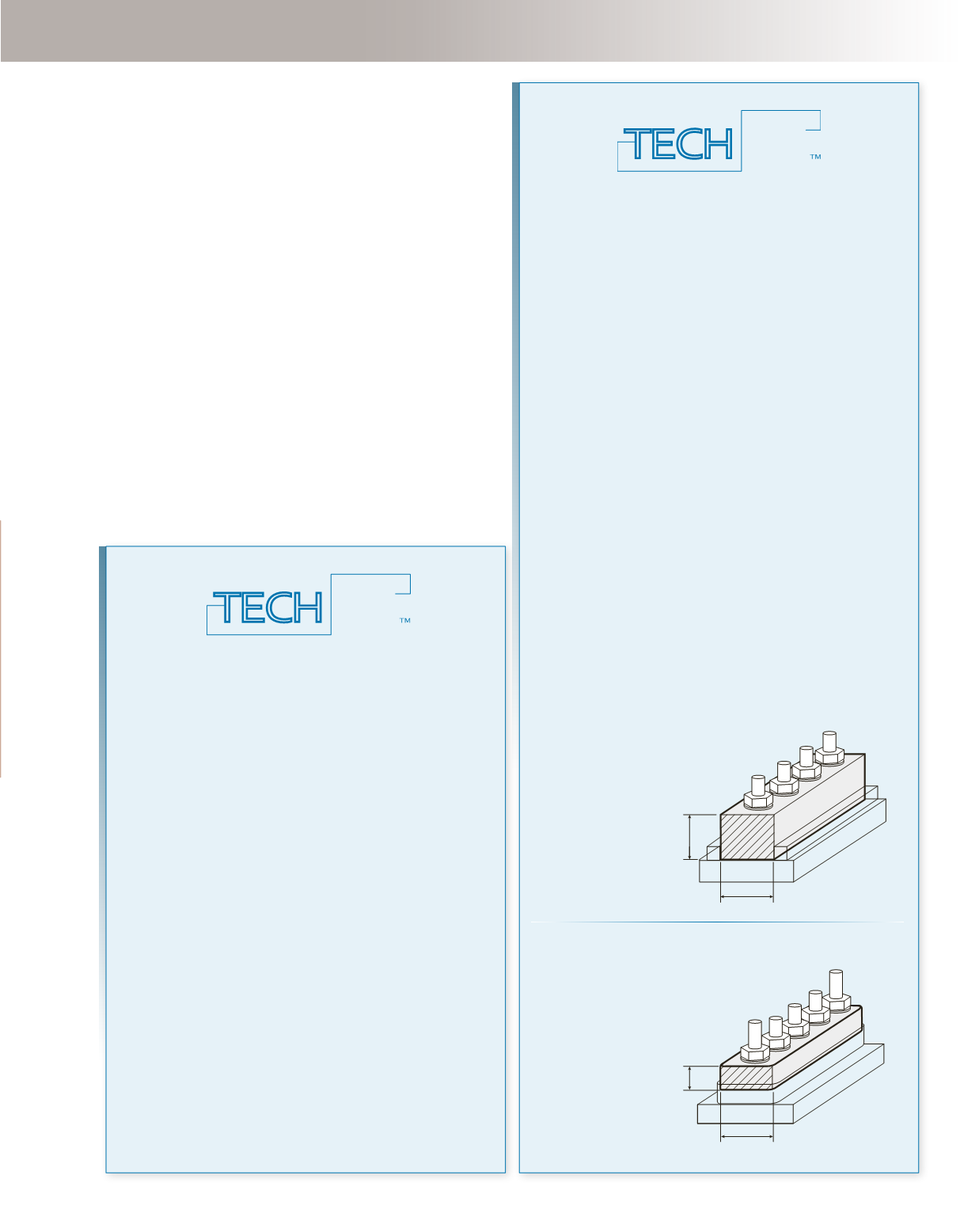
2) Cross Section:
A thicker cross section provides more material
for electron flow and a larger surface area for efficient cooling.
Carefully compare cross sections of a bus and do
not rely solely on published ratings.
19mm
25.5mm
7.5mm
25.5mm
Blue Sea Systems
BusBar Cross Section and
Ampacity Rating
19mm x 25.5mm = 484mm
Rating:
600A
Competitors
BusBar Cross Section and
Ampacity Rating
7.5mm x 25.5mm = 191mm
Published Rating:
650A
Application steps which improve busbar performance:
1) Optimize Current Flow:
the performance of a busbar can
be increased by attaching the primary feed wire to the center of
the busbar. The performance can be further increased by first
attaching the primary feed wire followed by the highest
load wire to the same terminal. This will allow the current to be
carried by the large cables and avoid sending all of the current
through the busbar. Although this will improve the performance
of the busbar, it does not change the actual ampacity rating of
the busbar and should not be used when comparing one
busbar to another.
2) Increase Voltage Capacity:
Most busbars have both an
amperage and voltage rating. Higher voltage can be
achieved by:
a.
Increasing the creepage distance, which is the distance from a
busbar mounting fastener to a grounded surface like a firewall.
Creepage distance directly impacts the voltage rating of the
busbar. Insulating the base and using insulating fasteners
rather than conductive fasteners will significantly increase
the safe operating voltage of a bus bar. The insulating system
including the creepage distance has to prevent failure in the
event of transients and surges in voltage.
b.
Managing the buildup of corrosion will significantly improve
the safety and service life of a busbar. No exposed busbar
can be expected to operate safely with a live connection in
a wet location. An exception would be busbars used for
lightening protection and grounding systems.