138
A P P E N D I X
DC Main Circuit Protection and
Branch Circuit Protection
Purpose
Fuses and circuit breakers are used to protect wire
insulation from melting and starting fires in the event of
overcurrents or short circuits which cause more amperage
to flow in a wire than that wire is rated to carry. It is
important to note that, except for those wires that are
intended to carry starting currents, every positive wire in
the DC Main Power Distribution System must be protected
by a fuse or circuit breaker.
Considerations for DC Main Circuit Protection
Mounting Placement—distance from power source.
The DC Main circuit protection system uses circuit breakers
or fuses to protect the wires of the DC Main distribution
system. The American Boat and Yacht Council (ABYC)
publishes voluntary standards for the type and placement
of the fuse or circuit breaker to be used as a DC Main circuit
protection device. Wire intended to carry engine starting
currents between the batteries, the switch, and the starter
is not required to have main circuit protection devices
installed. Maximum mounting placement dimensions for a
fuse or circuit breaker are 7" if the conductor is not housed
in a sheath or enclosure in addition to the wire insulation,
40" if the conductor is housed in a sheath or enclosure in
addition to the wire insulation, and 72" if the conductor is
connected directly to the battery and housed in a
sheath or enclosure in addition to the wire insulation.
Selecting DC Main Circuit Protection
The principal attribute of a DC Main circuit protection device
is its Ampere Interrupt Capacity (AIC) rating. Specifications
listed in the ABYC standards determine the AIC a DC Main
circuit protection device must have. The required AIC rating is
determined by the total CCA of the batteries connected to the
circuit. See the tables at right for the required AIC ratings.
Wire selection for DC applications on boats is usually
based on voltage drop requirements. However, there is a
maximum continuous current that the wire can withstand
without overheating. Higher grade marine wires are rated
for service up to 105°C (221°F)—the ABYC wire capacity
table for 105°C is most frequently quoted. The 105°C table
accurately reflects the capacity of single conductors exposed
to freely circulating cooling air. However, other factors, such
as covering bundles of wire in outer jackets to form a cable,
or use of conduits or structural voids to protect wires, can
reduce the cooling and reduce the safe capacity of the wire.
A more conservative strategy is to use the 105°C wire, but
treat it according to the 75°C table above when selecting
circuit protection unless the wire is openly exposed
for cooling.
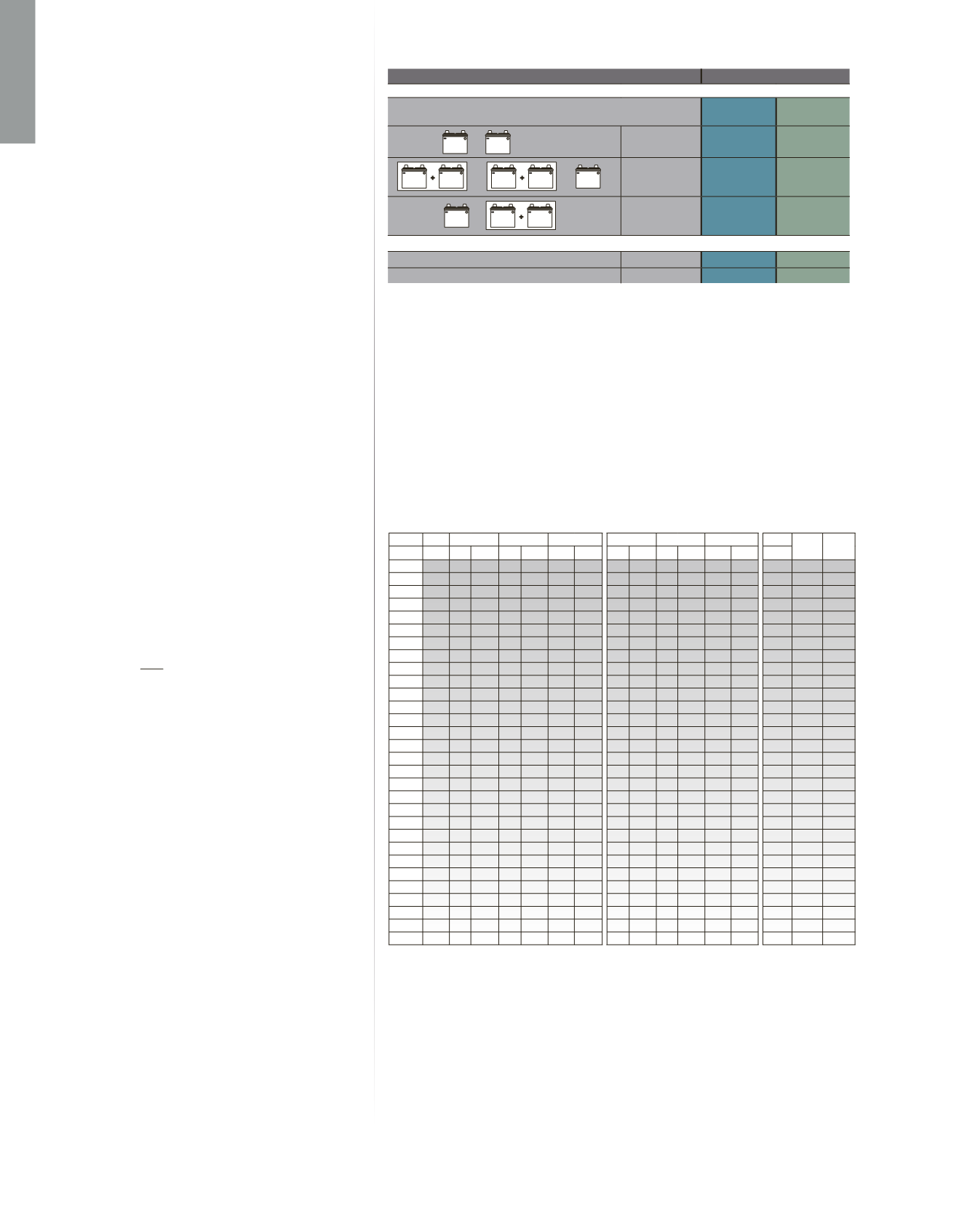
Total Connected Battery Cold Cranking Amperes (CCA) *
Ampere Interrupt Capacity
12 VOLTS AND 24 VOLTS
The white boxes identify two batteries, of the same size,
placed in parallel configuration.
DC MAIN
DC BRANCH
650 CCA or Less
1,500 AIC
750 AIC
651–1,100 CCA 3,000 AIC
1,500 AIC
Over 1,100 CCA 5,000 AIC
2,500 AIC
32 VOLTS
1,250 CCA or Less 3,000 AIC
1,500 AIC
Over 1,250 CCA 5,000 AIC
2,500 AIC
G24
G27
OR
OR
8D
4D
4D
OR
OR
G24
G24
G27
G27
4D
ABYC E-11 requires the use of circuit breakers that can be reused and reset and that they be
applied as per the table above. The standard does not strictly require that fuses be applied
in the same way, but it is an issue to consider, especially with high amp fuses used to protect
panel feeders or inverters. Fuses under 10 Amp rating generally have such a high internal
resistance they prevent fault currents from reaching 1000 Amps in 12 Volt circuits. The apparent
contradiction when using these fuses for bilge pumps and other circuits directly off the battery is
less of an issue than it might seem. If a fuse blows, and the case appears to be cracked or metal
has been ejected, the fuse holder should be replaced.
ABYC Interrupt Rating Table
† Thermally limited amperage capacity
See the Blue Sea Systems Circuit Wizard at circuitwizard.bluesea.com
or pages 133-135 for more assistance with wire and circuit
protection selection.
Standard Metric 75°C
90°C
105°C
75°C
90°C
105°C
Ohms
/1000ft
Ohms
/1000m
AWG mm²
EngRm
EngRm
EngRm
EngRm
EngRm
EngRm mm dia
0.75 9.5 7
19 15.5 19 16
6.6 5.0 13 11 13 11
0.98 7.29 23.92
18
0.82 10 8
20 16 20 17
7 5
14 12 14 12
1.02 6.67 21.88
1.0 13 10 21 17 21 18
9 7
15 12 15 13
1.13 5.47 17.94
16
1.3 15 11 25 21 25 21
11 8
18 14 18 15
1.29 4.17 13.70
1.5 16 12 24 20 29 24
11 9
17 14 20 17
1.38 3.65 11.96
14
2.1 20 15 30 25 35 30
14 11 21 17 25 21
1.63 2.63 8.63
2.5 21 16 34 28 38 32
15 11 23 19 26 22
1.78 2.19 7.18
12
3.3 25 19 40 33 45 38
18 13 28 23 32 27
2.05 1.65 5.42
4.0 34 25 46 38 51 43
24 18 32 27 35 30
2.26 1.37 4.49
10
5.3 40 30 55 45 60 51
28 21 39 32 42 36
2.59 1.04 3.41
6.0 53 40 57 47 65 55
37 28 40 33 45 39
2.76 0.91 2.99
8
8.4 65 49 70 57 80 68
46 34 49 40 56 48
3.27 0.65 2.14
10.0 79 60 84 69 100 85
56 42 59 48 70 60
3.6 0.55 1.79
6
13.3 95 71 100 82 120 102
67 50 70 57 84 71
4.1 0.41 1.35
16.0 105 79 113 93 134 114
73 55 79 65 94 80
4.5 0.34 1.12
4
21 125 94 135 111 160 136
88 66 95 78 112 95
5.2 0.26 0.85
25 141 106 150 123 175 148
99 74 105 86 122 104 5.6 0.22 0.72
3
27 145 109 155 127 180 153
102 76 109 89 126 107 5.8 0.21 0.67
2
34 170 128 180 148 210 179
119 89 126 103 147 125 6.5 0.16 0.53
35 173 130 186 153 217 185
121 91 130 107 152 129 6.7 0.16 0.51
1
42 195 146 210 172 245 208
137 102 147 121 172 146 7.3 0.13 0.42
50 220 165 235 193 273 232
154 116 164 135 191 163 8.0 0.109 0.36
0
54 230 173 245 201 285 242
161 121 172 141 200 170 8.3 0.102 0.34
00
68 265 199 285 234 330 281
186 139 200 164 231 196 9.3 0.081 0.27
70 274 206 292 239 341 289
192 144 204 168 238 203 9.4 0.078 0.26
000
85 310 233 330 271 385 327
217 163 231 189 270 229 10.4 0.064 0.21
95 334 251 357 293 413 351
234 175 250 205 289 246 11.0 0.058 0.19
0000 107 360 270 385 316 445 378
252 189 270 221 312 265 11.7 0.051 0.17
120 387 290 414 339 478 406
271 203 290 237 335 284 12.4 0.046 0.15
150 445 333 476 390 550 467
311 233 333 273 385 327 13.8 0.036 0.12
REFERENCE DATA
WIRE SIZE
ABYC Ampacity Rating Table at 30°C
TEMPERATURE RATING OF CONDUCTOR INSULATION
Data based on E-11 Table VI-A
(Single Conductors in Free Air)
Data based on E-11 Table VI-B
(Up to three conductors in a sheath,conduit or bundle)
SAE conductors are smaller than equivalent AWG by 5% to 12% with current capacity typically
less by 7%.
ISO Ratings for metric wire are slightly less than these values derived from ABYC VI-A ratings.
• For bundles of 4 to 6 conductors multiply by 0.857
• For bundles of 7 to 24 conductors multiply by 0.714
• For bundles of 25 or more, conductors multiply by 0.571
Wires counted in bundles need not include:
1. Wires carrying intermittent currents no more than rating per VI-A and for less than one minute
per mm of diameter, and not repeating more often than a delay of 5X times active duration.
2. Wires carrying load currents at less than 50% of the wire rating per table VI-B.
* Battery cold cranking performance rating at -17.8°C (0°F): The discharge load in amps that a battery at -17.8°C (0°F)
can deliver for 30 seconds, and maintain a voltage of 1.2 Volts per cell or higher, (e.g. 7.2 Volts for a 12 Volt battery).
The CCA for the battery icons in this chart is an approximation and could be slightly higher or lower. Consult the battery
manufacturer’s specifications for precise CCA ratings. A battery rated in MCA will have a CCA capacity approximately
80% of MCA